
Have you ever read an email and wondered if it truly came from the listed sender? If so, it may be email spoofing. To learn more about email spoofing, follow this guide.


Email spoofing definition
Email spoofing is a practice used in scams and phishing attacks to deceive people into believing the message came from a known or trusted source.
Have you ever opened an email from someone you know only to be unsure if it was them who wrote the message?
Whether it seems like a spam email or they asked you a personal question they already know the answer to, it's possible the sender may not be who they appear to be.
How, you ask? The answer is email spoofing.

Email spoofing is a practice used in scams and phishing attacks to deceive people into believing the message came from a known or trusted source. Cybercriminals use this technique hoping that the recipient will not notice and engage with the message as if it’s a legitimate email.
But before you start second-guessing every email you’ve ever received, read through this complete guide where we’ll cover how email spoofing works, what it looks like, and how you can protect yourself from it.
In simple terms, the goal of email spoofing is to make the recipient believe the email is coming from someone they can trust. Then the attacker exploits that trust, whether they use it for phishing, spreading different types of malware, or tarnishing the sender's reputation. To help you understand how email spoofing works, here are three different ways an email spoofer may try to trick you.
Display name spoofing is an example of spoofing email headers where only the sender’s display name is falsified. With this type of email spoofing, the email address itself will not match the display name attached to the email. For example, you may get an email that says it is coming from your boss, but after opening the message, you notice that the sender’s email address does not match your boss’s.
This is possible if a cybercriminal creates a new email address under your boss’s name. Because the email itself is legitimate, this type of spoofed email might bypass any spam filters, therefore easily making it into your inbox.
Legitimate domain spoofing is a much more believable email spoofing example. In this case, both the display name and the sender’s address will be fake. Cybercriminals can do this by taking advantage of Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), which is an email protocol used for sending messages.
During normal email communications, your email client (Gmail, Outlook, etc.) will automatically enter the sender’s address whenever an email is sent. In the event of email spoofing, the attacker can manipulate this information, making it seem as if the email is coming from someone else. Because SMTP does not provide a way to authenticate email addresses, the scammer can manually change the “To,” “From,” and “Reply To” fields when sending spoofing emails.
Another example of email spoofing is the use of look-alike domains. An example of a spoofed domain is “amaz0n.com.” In this specific scenario, the spoofer created a domain attempting to impersonate “amazon.com.” At first glance, you may not notice that the “o” has been replaced with a “0.”
This technique can be effective if you don’t pay close attention to the spoofed email header, especially if the contents of the email look legitimate. Because of this, it’s important to always pay close attention to the sender’s details before engaging with an email.
At first glance, email spoofing may sound a lot like phishing, and in some cases, the two do involve each other. But these two cybersecurity threats are different. Phishing is another type of cyberattack utilized by cybercriminals to try and lure sensitive information from you. This can take place over text, email, social media, or on the phone (an attack also known as vishing).
No matter where this attack takes place, the main goal of phishing is to access your personal information for fraudulent activities such as identity theft. Email address spoofing may play a crucial role in these attacks, allowing the cybercriminal to appear as if they are somebody else.
But phishing isn't the only reason a cybercriminal may use email spoofing to their advantage. Let’s look at some other reasons for email spoofing.
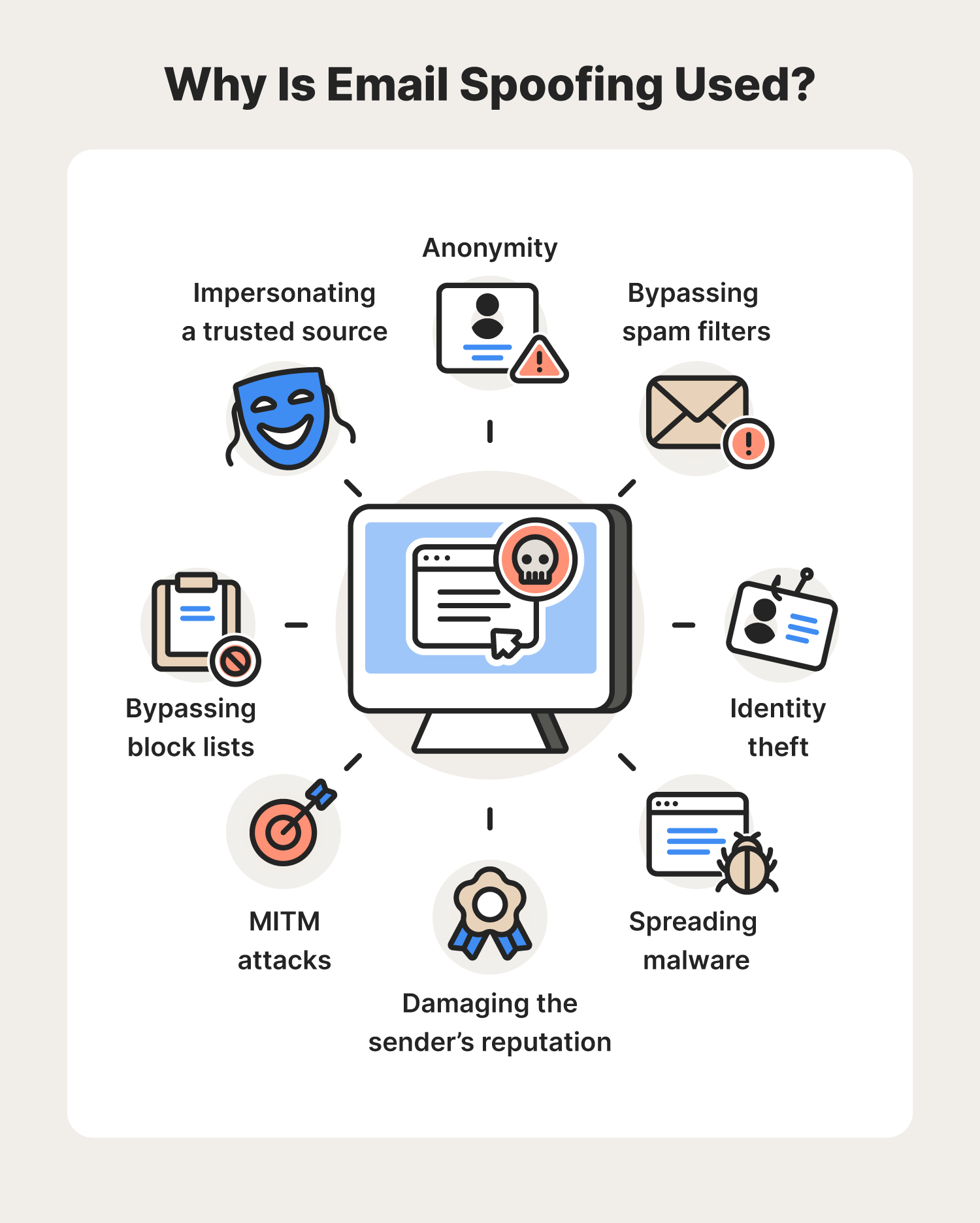
As you can see, there are many reasons why a cybercriminal might use email spoofing to their advantage. But how does email spoofing work?
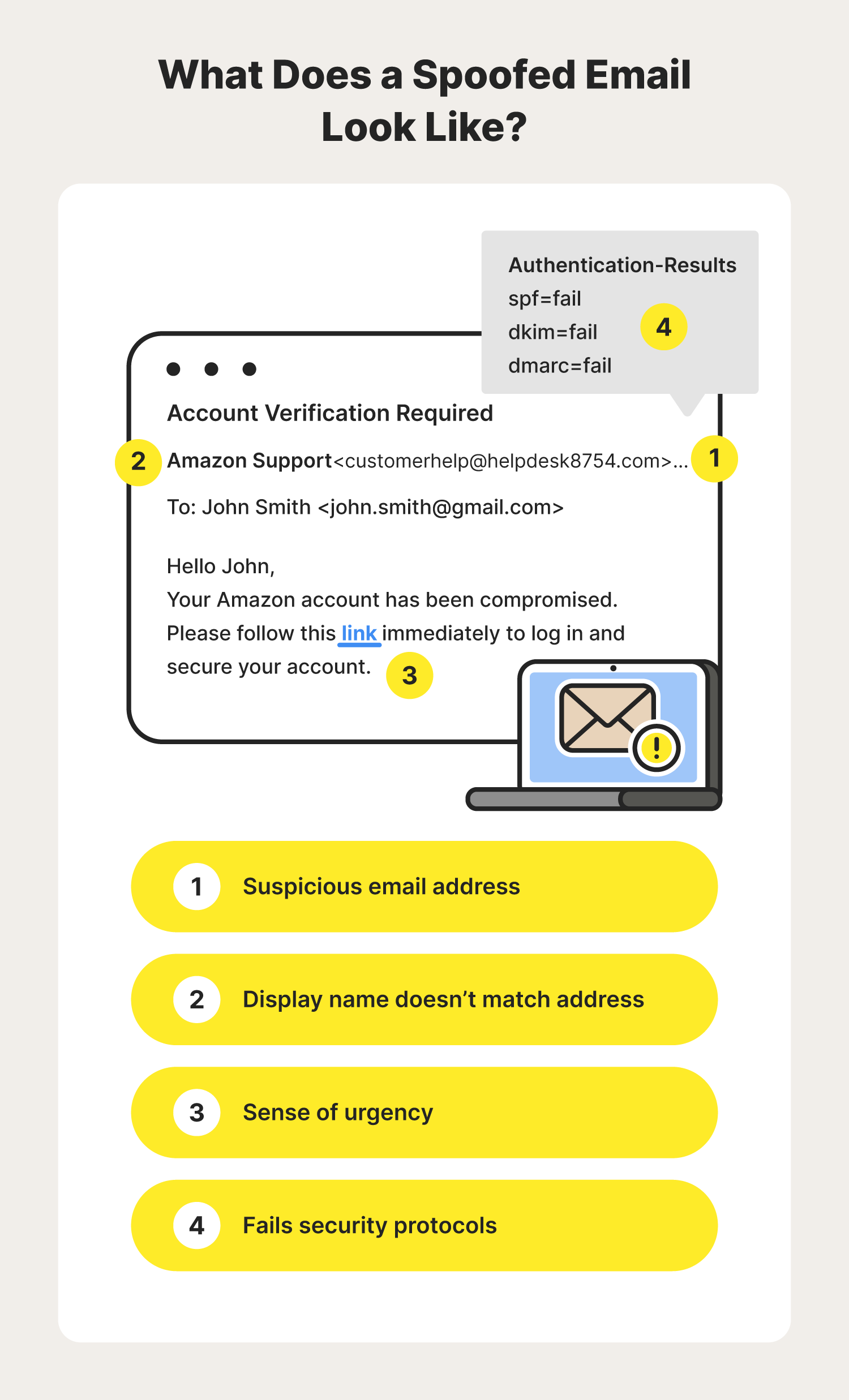
Now that you know the different ways an email spoofer could try to impersonate another sender, you may be wondering how you can quickly spot a spoofed email.
Whenever you come across an email you’re unsure about, keep an eye out for these warning signs.
While it's possible that not every spoofing email will show these signs, carefully analyzing the sender’s address and display name can help you catch some spoofed emails that may have made it to your inbox. Fortunately, most popular email providers have put additional security frameworks in place to help detect spoofed emails, including:
Not only do these security measures help alert users of spam and spoofed emails, but they can be used to help verify if an email is legitimate. To learn how you can use these security protocols to check the legitimacy of a message, follow the following steps based on your email provider.
How to check SPF, DKIM, and DMARC status on Gmail:
How to check SPF, DKIM, and DMARC status on Outlook:
How to check SPF, DKIM, and DMARC status on Yahoo Mail:
By taking these additional precautions, you can be sure that you’re dealing with a legitimate sender, therefore reducing the risk of a spoofed email address going unnoticed.
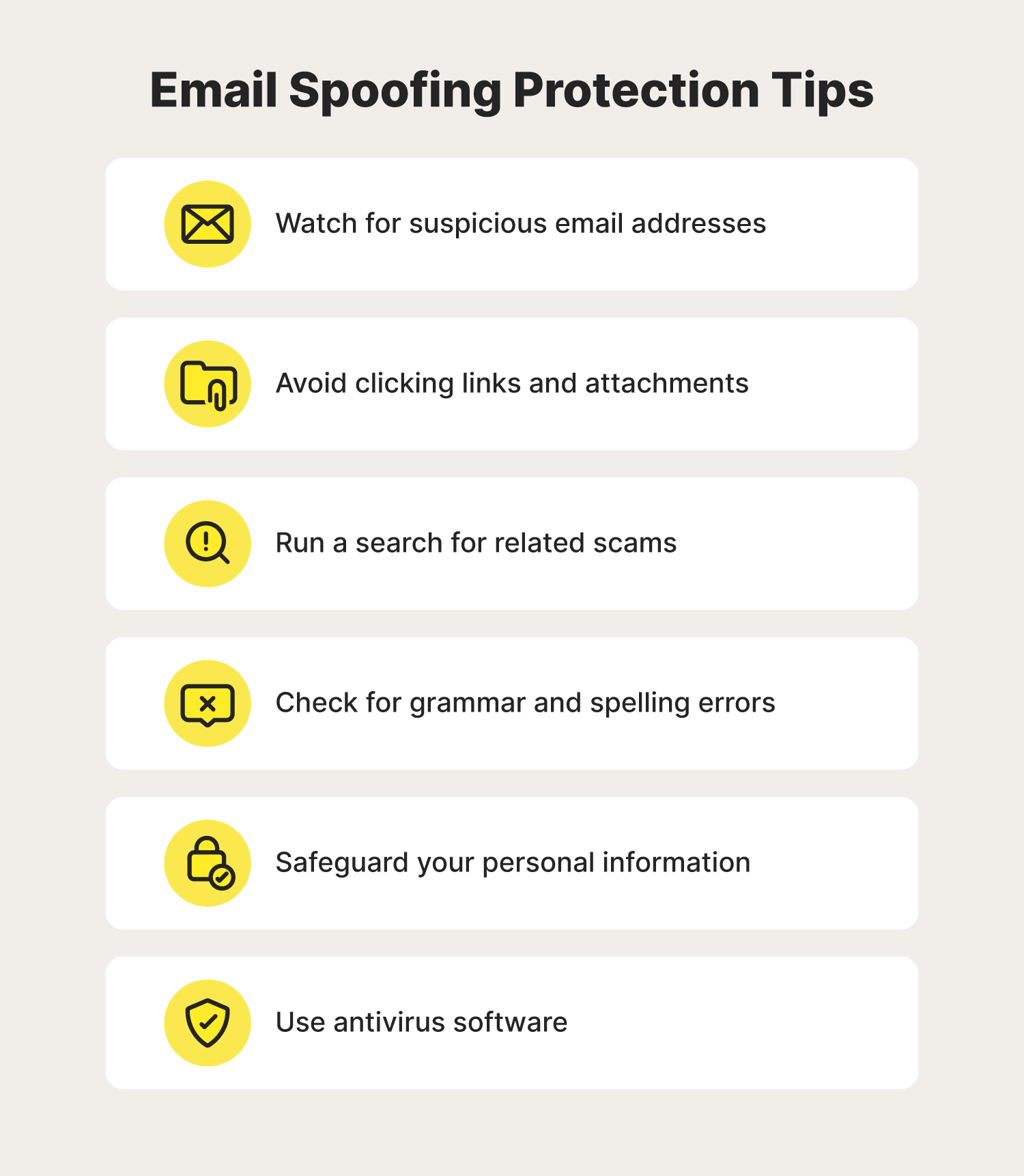
In addition to doing your best to identify a spoofed email before responding, there are precautions you can take to protect yourself from email spoofing. To help keep yourself Cyber Safe while using email, follow these protection tips:
Now that you have a better understanding of email spoofing and how you can protect yourself against it, you can follow up, circle back, and send with confidence. Above all, it’s important to always use common sense and be cautious, as there are other threats that can impact your email security.
Still have more questions? We’ve got answers. Read along to learn answers to these commonly asked questions about email spoofing.
The difference between a spoofed and hacked email account is that a hacked account means that the hacker has gained full access to your email account, allowing them to send legitimate messages from your address. In the event that your email address is spoofed, the hacker will only be attempting to make it look as if the message is coming from you, but they won't have access to your account.
Generally speaking, yes, email spoofing can be traced. This is due to a security protocol known as Sender Policy Framework (SPF), which can locate the sender’s IP address.
Unfortunately, there is no way to completely prevent cybercriminals from attempting to use your email address. However, there are precautions you can take to prevent a scammer from logging into your email account, such as using strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication.

7 days of FREE* comprehensive antivirus, device security and online privacy with Norton Secure VPN.
Join today. Cancel anytime.
*Terms Apply

Clare Stouffer, a Gen employee, is a writer and editor for the company’s blogs. She covers various topics in cybersecurity.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.